How does the greenhouse effect work?
As you might expect from the name, the greenhouse effect works … like a greenhouse! A greenhouse is a building with glass walls and a glass roof. Greenhouses are used to grow plants, such as tomatoes and tropical flowers.
A greenhouse stays warm inside, even during the winter. In the daytime, sunlight shines into the greenhouse and warms the plants and air inside. At nighttime, it's colder outside, but the greenhouse stays pretty warm inside. That's because the glass walls of the greenhouse trap the Sun's heat.
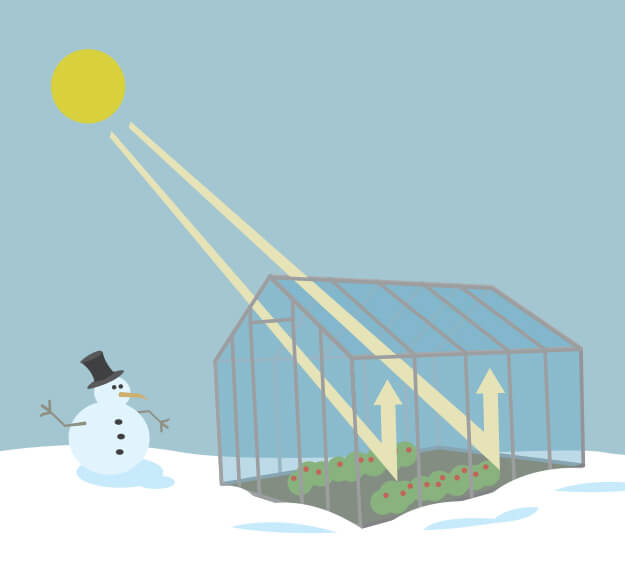

A greenhouse captures heat from the Sun during the day. Its glass walls trap the Sun's heat, which keeps plants inside the greenhouse warm — even on cold nights. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth. Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat similar to the glass roof of a greenhouse. These heat-trapping gases are called greenhouse gases.
During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere. Earth's surface warms up in the sunlight. At night, Earth's surface cools, releasing heat back into the air. But some of the heat is trapped by the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. That's what keeps our Earth a warm and cozy 58 degrees Fahrenheit (14 degrees Celsius), on average.
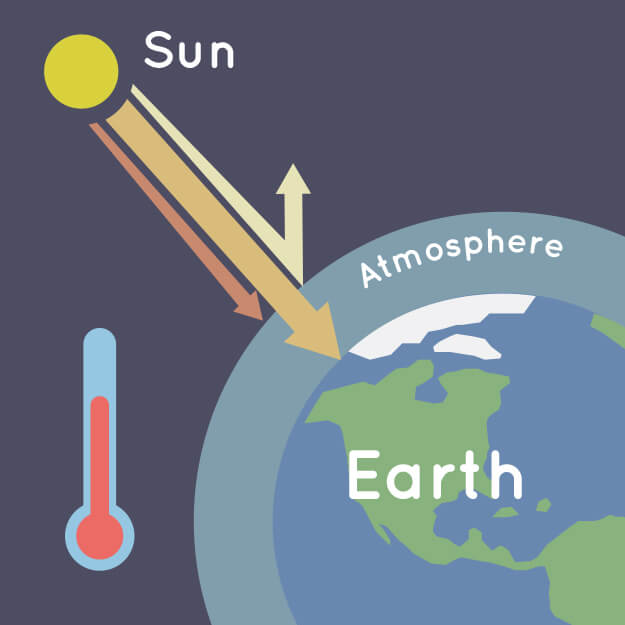
Earth's atmosphere traps some of the Sun's heat, preventing it from escaping back into space at night. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
How are humans impacting the greenhouse effect?
Human activities are changing Earth's natural greenhouse effect. Burning fossil fuels like coal and oil puts more carbon dioxide into our atmosphere.
NASA has observed increases in the amount of carbon dioxide and some other greenhouse gases in our atmosphere. Too much of these greenhouse gases can cause Earth's atmosphere to trap more and more heat. This causes Earth to warm up.
What reduces the greenhouse effect on Earth?
Just like a glass greenhouse, Earth's greenhouse is also full of plants! Plants can help to balance the greenhouse effect on Earth. All plants — from giant trees to tiny phytoplankton in the ocean — take in carbon dioxide and give off oxygen.
The ocean also absorbs a lot of excess carbon dioxide in the air. Unfortunately, the increased carbon dioxide in the ocean changes the water, making it more acidic. This is called ocean acidification.
More acidic water can be harmful to many ocean creatures, such as certain shellfish and coral. Warming oceans — from too many greenhouse gases in the atmosphere — can also be harmful to these organisms. Warmer waters are a main cause of coral bleaching.
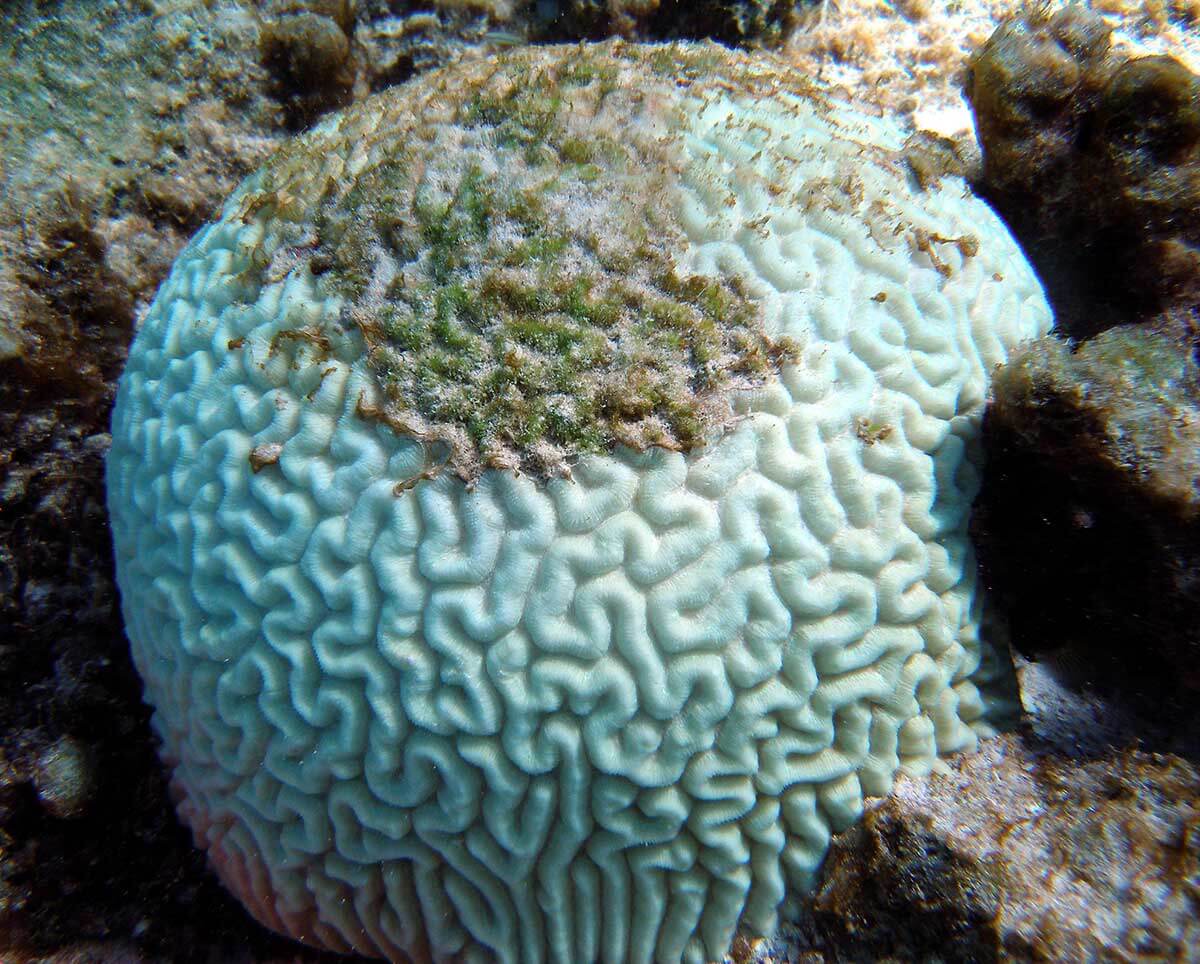

This photograph shows a bleached brain coral. A main cause of coral bleaching is warming oceans. Ocean acidification also stresses coral reef communities. Credit: NOAA







